How to install Security Onion
Download security onion iso - https://github.com/Security-Onion-Solutions/securityonion/blob/master/VERIFY_ISO.md
Docs of security onion - https://docs.securityonion.net/en/2.3/
What is security onion
- Security onion is a Network Security Monitoring system that monitors the network for security events, helps identify vulnerabilities or Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificates and assists in the process of active and or reactive incident response and network forensics. The NSM helps provide context, intelligence and situational awareness of the network. The ESM (Enterprise Security Monitoring) system provides additional settings with endpoint visibility and telemetry from within the environment.
What is North-South traffic
- When communication between components in a data center and another system which is physically out of the data center. Any traffic coming to a data center or going out of it to another system which can be a client requesting access to a web application as an example.
Traffic moving downstream of the modem through the firewall to its destination is called southbound traffic.
Traffic moving upstream from the server/virtual machine upstream through the router, firewall and to the modem is northbound traffic
The northbound and southbound traffic usually happens with queries, commands and data being exchanged throughout a data center.
What is East-West traffic
- When two or more components of a data center or between many other data centers communicate with one another. This happens when traffic is routing from a data center over a LAN communication to another server in a different data center
How Security onion works
- Security onion sits in an environment with a Modem, firewall, router, workstations, servers, virtual machines and much more. It can monitor traffic north and south to detect active adversary, (potential threat actors) attempting to establish a Command and Control (C2) within the environment or even detect when data exfiltration is happening within the network. You can also monitor East and West traffic
This system is meant for Monitoring the traffic in your environment to ensure you see what is moving around in the network. It’s not perfect nor is it accurate since it’s automated and can be configured, but having the ability to trace the network traffic, analyze it further and understand the outcome of each event will need to happen for any defender. This software works as an Intrusion Detection system, can view and parse network metadata, includes the ability to have packet capture of your network, file analysis and can have Intrusion Detection honeypots.
Intrusion Detection System
- Security onion genereates a Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) alerts by looking for specific fingerprints and identifiers from known malicious, anomalous/suspicious traffic within the network. The signature based system can generate alerts through a system called Suricata where we are able to also make our own Intrusion Detection System rules within Suricata.
Link to Suricata documentation - https://docs.suricata.io/en/latest/configuration/suricata-yaml.html
Full Packet Capture
- With the ability of running packet captures throughout your network, you have the ability to go back to alerts, parse the data, follow the tcp stream or even confirm and see where data is moved with either file exfiltration or even running possible malicious activity attempts from possible adversarys.
Updating Security Onion
- The way to update the Security Onion OS and overall the system is to only run the command sudo soup as this will check for all fixes within the CentOS 7 and for Security Onion itself
Now that you have a bit of an understanding of how Security Onion functions and operates, lets begin the installation process
Github to the iso file - https://github.com/Security-Onion-Solutions/securityonion/blob/master/VERIFY_ISO.md
What I personally use to create a bootable media for on a USB drive is with balena etcher
Link to Balena etcher - https://etcher.balena.io/
Recommended hardware for the Security onion standalone installation
RAM – 12 GB
CPU Cores – 4
Storage – 200 GB
My hardware configuration
Server – Dell Poweredge T310
CPU Cores – 4
Storage – 500 GB HDD
RAM – 16 GB
NIC count (1 GB speeds) – 14
Insert the USB with the Security onion bootable media installed
Boot into the Bootable menu with the F10 key when shown on the top right corner
When prompted, select the F1 key to continue
When prompted, go to the Hard Disk option
It will automatically pop options open for media to choose, select your Front USB: USB option
With the bootable media inserted into the server, select the option
Install Security Onion 2.3.250
After choosing the installation method, you will notice it says Welcome to CentOS Linux 7 (Core)!
Security onion is managed upstream within the core function.
Installation begins when this is shown
Create your own admin user account that will be able to sign into the Security Onion terminal
Ensure to use a strong password
The installation process will begin, this can take upwards to 15 minutes at some times and may cause the machine to sleep.
If the machine goes into a sleep mode, you can press the enter key to wake the machine during the installation process
When prompted, press the enter key to reboot the server
You will then notice a new prompt of 2 choices of CentOS linux on the installation process
Press the first option of the CentOS Linux that isnt the rescue version but with Core
Sign into the Security onion machine with the credentials you made within the initial installation
You will then be prompted with the welcome screen of Security Onion
Select Yes that you would like to continue onward
Select the option to install the Standard Security installation method
You can hover over the Install option and then press Tab to the ok option to confirm
This will be the way to confirm your choice
Select the STANDALONE production installation method of Security onion
You can select it by using the arrow keys over your option and pressing the Enter key to confirm
Type the word AGREE to agree to the terms of the Elastic license
Type the hostname you would like the security onion to be named as
My hostname is siem-securityonion
Enter the description you would like this software to be as
Mine is homelab-siem because it will be used within my homelab
Select the NIC you would like for your management interface
This NIC will be used so you can gain access to the dashboard and manage Security Onion
Select Static for configuring your Static IPv4 address
Input an IPv4 address in CIDR notation that is used on your management network for you to gain access to the web user interface
IPv4 address – 192.168.80.50/24
Enter the default gateway within the subnet
Default gateway – 192.168.80.254
Input your DNS servers for your Security Onion and seperate them with commas
Note – Do not put a space after each IP address for the DNS server
DNS Servers used:
8.8.8.8
8.8.4.4
9.9.9.9
Enter a DNS search domain of your requirements, I left mine as default
Select Ok to initialize the networking
Select the choice of your requirements used
I am using a Standard installation method because it will have internet access
Select the process of how you are going to connect to the internet
I don’t have a proxy so I will be choosing Direct
It will now prompt the preflight checks of the system requirements
Select the NICs for your monitoring interface
This will go to every single subnet you are monitoring and not every single physical device
Choose your OS update method. This wont update the packages for security onion tools such as Zeek (BRO), Elasticsearch, Kibana, Saltstack, etc
I use a manual update method
Input all of the subnets within the network with CIDR notation and seperating with commas.
Don’t put any spaces after the commas when entering the subnets
Example – 192.168.1.0/24,192.168.40.0/24
Choose the Basic installation method with the recommended settings
Choose how you would like to generate metadata.
I will be using Zeek (use to be known as Bro) for metadata and Suricata for the Network Intrusion Detection (NIDS) Alerts
Choose the services you would like to run within Security Onion and this will take more RAM and processing power when in use
I will be using all 4
OSQuery
Wazuh
Playbook
Strelka
Accept the default IP range within docker or configure to your requirements
I selected Yes to accept the defaults
Input an email or username for the administrator account on Security Onion
This will be used to sign into the web user interface of Security Onion
Enter a password for your Security onion account and ensure to retype the password on the next prompt
Choose the method of choice you would like to access the web user interface of your Security Onion machine
I will be using a IP address based system
Select Ok to set a password for the soremote user account which is used for adding sensors remotely
Enter a strong password for the soremote user account and ensure to confirm it afterwards
Select the Basic installation of the Network Security Monitoring components with the recommended settings
Since I will be using Zeek (BRO) for my metadata, I will be using 1 Zeek process
I will be using Suricata as my NIDS alerts, I will need 1 Suricata process
Select Yes to configure the NTP server
Input the NTP server IP address you are hosting or NTP Server pools you need
Use the NODEBASIC install for search node with recommended settings
Input a single IP address or IP address range in CIDR notation to allow you to access the web user interface
Example 1 – 192.168.1.0/24 will allow the whole subnet to access it
Example 2 – 192.168.70.25/24 will allow the one IP address to access the web user interface
Verify your configuration and select Yes to continue the installation
Installation begins
When finished, it will then prompt you to press enter to reboot the machine and navigate to the IP address to go into the management interface of Security Onion, but we will updating Security Onion prior to doing so
Sign into your user account
Type the command below to run the Security Onion Updater (SOUP)
Command – sudo soup
The Security Onion Updater has successfully finished with no errors
Run the command below to verify all services are running on Security Onion
Command – sudo so-status
Navigate to the IP address you are going to use for the Security onion interface
Select Advanced and choose to proceed
Example link to the web user interface – https://192.168.1.1
Sign into the security onion web user interface with the email you made
The Security Onion welcome/overview screen
The Alerts tab will show all the alerts generated from Suricata
The Dashboard will show all the information within Security Onion
The Hunt tab is where you can escalate alerts from your system and can escalate issues to your Cases to follow any potential malicious activity
When escalating alerts to a new case, it will go into the Cases tab for further analysis
The PCAP tab is where we can run a PCAP analysis of your network to find out if there are any potential suspicious activity unseen within the environment and can export if needed for later analysis.
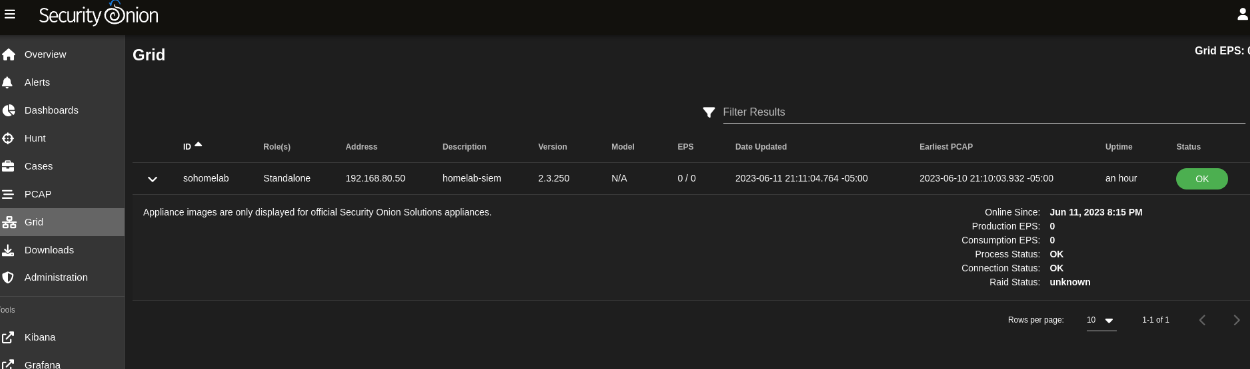
The Grid tab shows information of all Security Onion nodes and there status
The Downloads tab shows all the utilities and packages you can configure with Security Onion and integrate it with other systems
The Administration > Users tab shows a list of users that are added into the Security Onion Console (SOC) web user interface
Elastic is where you can breakdown and look more in depth in regards to network traffic analysis
Grafana is used for alerts, system utilization monitoring and graphing what your traffic usage is outbound and inbound
Cyberchef is self hosted on Security onion and can assist in decoding, encoding, hashing/dehashing and much more
Playbooks generates alerts on the Dashboard, Hunt or Kibana menus depending on the severity level on the Playbook configuration
Fleet is used for vulnerability reporting, detection engineering, Device management, device health monitoring, posture-based access control, managing unused software licenses and much more.
Mitre attack/navigator tool shows the planning for either the Blue or Red team to create a plan of execution. This can be changed and modified with color coding or numerical values to the end users preferences.